Knee Injuries from Tennis: Best Treatment for Tennis Knee Injury

Tennis is a fast-paced, exhilarating sport that demands agility, precision, and endurance from its players. However, amidst the thrilling backhands and powerful serves, lies a common adversary for many tennis enthusiasts – Knee Injuries from Tennis. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or an occasional player, the risk of developing a tennis knee injury looms large. From overuse to sudden twists and turns on the court, the causes of these debilitating injuries are as diverse as they are concerning. But fear not! In this comprehensive article, we will explore the underlying reasons behind knee injuries from tennis and delve into effective treatment options to help you bounce back onto the court with confidence.
As you step onto the pristine blue court with your racket in hand, it’s easy to overlook the potential strain your knees endure during each lightning-quick movement. The distinctive sound of shoes squeaking against the hard surface becomes a symphony of determination and skill – but at what cost? This article aims to unravel the mysteries surrounding tennis-related knee injuries by dissecting their origins and presenting practical solutions for recovery. So whether you’re an avid fan of baseline rallies or a casual weekend player looking to safeguard your knees from harm, join us on this enlightening journey through the world of tennis knee injuries.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Tennis Knee Injury
- 2 The Anatomy of the Knee
- 3 Common Knee Injuries in Tennis Players
- 4 Causes and Symptoms of Tennis Knee Injury
- 5 Prevention Strategies for Tennis Knee Injuries
- 6 Treatment Options for Tennis Knee Injuries
- 7 Rehabilitation and Return to Play
- 8 FAQ’s
- 9 Conclusion: Knee Injuries from Tennis
Understanding Tennis Knee Injury

The mystery behind tennis knee lies in understanding why it doesn’t affect all players equally. Factors like playstyle, technique precision, shoe choice, and genetic predisposition can determine vulnerability. But rest assured, knowledge is power! One can mitigate risk and foster longevity in the game they love passionately by understanding tennis knee injuries—their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures.
The Anatomy of the Knee
The knee is an incredibly complex joint comprised of numerous interconnected structures that enable a wide range of movements. At its core, the knee consists of three prominent bones: the femur (thigh bone), the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (kneecap). These bones are held together by a network of ligaments, including the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). These provide stability and support during dynamic activities such as playing tennis. In addition, two crescent-shaped pieces of cartilage called menisci act as shock absorbers, cushioning the joint and helping to distribute weight evenly.
Furthermore, the knee joint also houses a series of fluid-filled sacs known as bursae that reduce friction between moving parts, allowing for smooth motion. However, despite its rigid design, the knee is susceptible to injuries from sudden twists or impact joints in sports like tennis. Understanding this anatomy can help athletes appreciate the importance of proper conditioning and technique to prevent debilitating knee injuries and play at their best level.
Common Knee Injuries in Tennis Players
Tennis players are highly susceptible to knee injuries due to the repetitive stress on their knees from sudden stops, pivots, and quick directional changes. One common knee injury among tennis players is patellar tendinitis or jumper’s knee. This overuse injury results from the constant jumping and landing during serves and volleys. Additionally, meniscus tears are prevalent among tennis players due to the twisting movements involved in the game. These tears can cause pain and swelling in the knee joint, affecting a player’s mobility on the court.
An often overlooked but significant knee injury in tennis is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear. This type of injury usually occurs during abrupt deceleration or sudden direction changes while playing. ACL tears can be debilitating for tennis players and may require extensive rehabilitation or even surgical intervention for recovery. Tennis athletes must prioritize preventive exercises, proper technique, and wearing supportive footwear to minimize the risk of these common knee injuries.
7 Common Knee Injuries in Tennis Players
- Patellar Tendinitis (Jumpers Knee): Caused by repetitive strain on the patellar tendon, this injury leads to knee pain and inflammation, often seen in tennis players who jump and pivot frequently.
- Meniscus Tears: Sudden changes in direction or pivoting can result in tears in the knee’s meniscus cartilage, causing pain, swelling, and restricted movement.
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries: The ACL, crucial for knee stability, can tear during quick stops or pivots in tennis, leading to severe pain and the need for surgical intervention.
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Sprains: Injuries to the MCL can occur from lateral impacts or awkward landings, causing pain and instability in the knee joint.
- Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome: The ITB, running along the outer thigh, can become irritated due to repeated knee flexion and extension in tennis, resulting in lateral knee pain.
- Chondromalacia Patellae (Runner’s Knee): Tennis players can experience this condition where the cartilage under the kneecap softens, leading to pain and discomfort during play.
- Osteoarthritis: Over time, the wear and tear from tennis can contribute to knee osteoarthritis, causing chronic pain and reduced joint function.
Preventing these knee injuries in tennis requires proper conditioning, warm-up routines, and using appropriate footwear. If you experience knee pain or injury symptoms, consult a medical professional for evaluation and treatment to ensure a safe return to the court.
Causes and Symptoms of Tennis Knee Injury
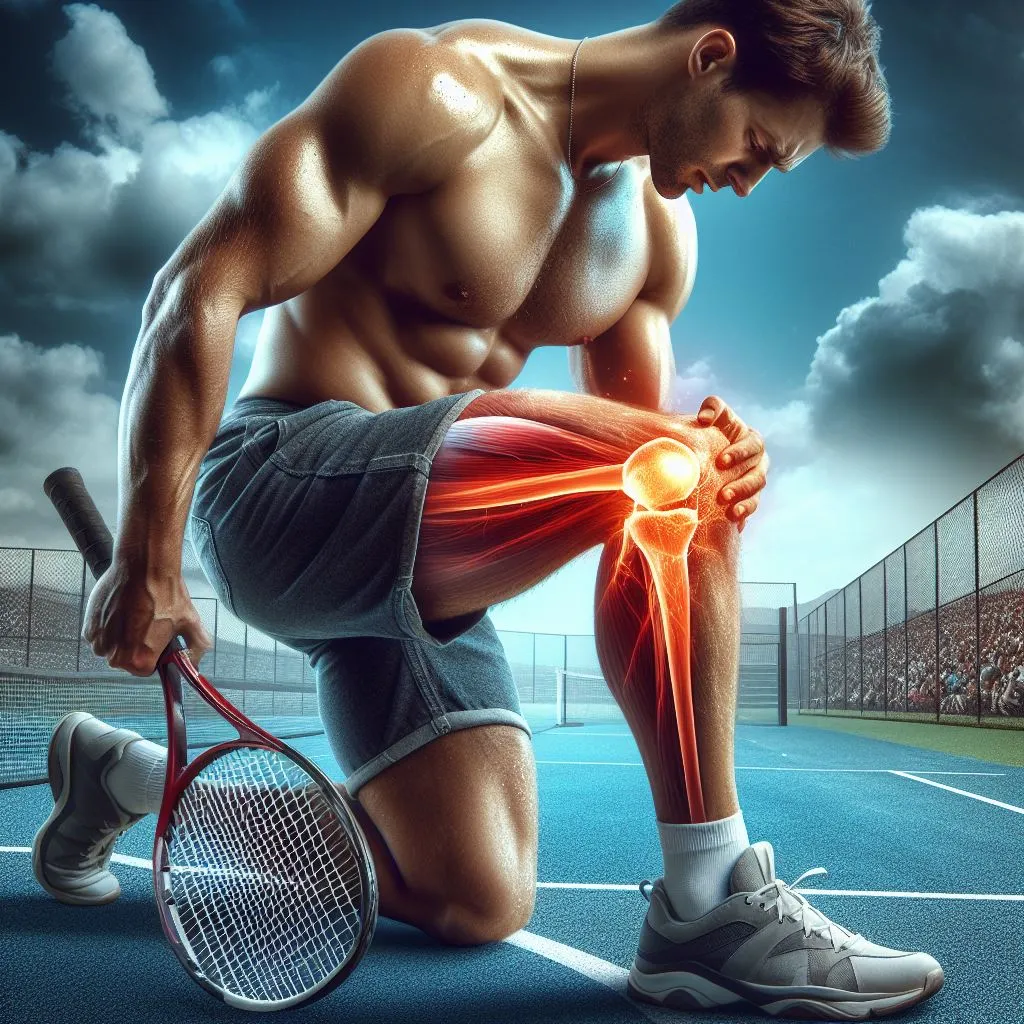

Symptoms of a tennis knee injury may manifest as pain and tenderness along the sides of the kneecap, swelling, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg. In some cases, individuals may experience a popping sensation or a feeling of instability in the knee. Attention to these signs is crucial, as they could indicate underlying damage or inflammation that needs prompt attention.
Prevention Strategies for Tennis Knee Injuries
Tennis knee injuries are common among players of all levels, but various prevention strategies can help mitigate the risk. Firstly, focusing on proper warm-ups and stretching before hitting the court is essential. This prepares the muscles and joints for intense activity and reduces the likelihood of sudden strain or injury during play. Additionally, paying attention to your form and technique while playing tennis is crucial. Maintaining correct posture, footwork, and movement patterns can significantly decrease the stress placed on the knees, ultimately reducing the risk of injury.
Furthermore, investing in supportive footwear specifically designed for tennis can make a notable difference in preventing knee injuries. A good pair of tennis shoes with proper cushioning and arch support helps absorb impact and provides stability during the quick lateral movements inherent in tennis. Moreover, cross-training exercises that strengthen the leg muscles without overloading the knees can contribute to injury. Prevention. Incorporating activities like cycling, swimming, or resistance training into your fitness regimen builds overall strength while giving your knees a break from repetitive impact.
Treatment Options for Tennis Knee Injuries
Physical therapy is one of the most effective treatment options for tennis knee injuries. A tailored exercise program can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and correct any imbalances that may have contributed to the injury. Additionally, physical therapists can guide proper technique and form during tennis activities to prevent further strain on the knee.
Another promising treatment option for tennis knee injuries is regenerative medicine, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. This cutting-edge approach involves injecting concentrated platelets from your blood into the injured area to promote healing and reduce inflammation. As a non-surgical alternative, PRP therapy has shown positive outcomes in helping athletes recover from tendon and ligament injuries. It is a valuable option for those with persistent tennis-related knee issues.
Rehabilitation and Return to Play
Returning to play after a tennis knee injury requires patience and careful planning. Rushing back into intense tennis play too soon can lead to setbacks or exacerbate the injury. It’s essential for players to gradually reintroduce themselves to on-court activities, starting with light drills before progressing toward full matches. Working closely with healthcare professionals and coaches is vital during this phase to ensure a safe transition back into regular play without compromising recovery progress. Patience, dedication, and a strategic approach are critical elements in rehabilitating a knee injury sustained during tennis.
FAQ’s
What is the most common knee injury in tennis?
Tennis players frequently sustain meniscus tears and patellar tendinitis in their knees. Repetitive strain on the patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap to the shinbone, results in patellar tendinitis, often known as jumper’s knee. Because of the frequent twisting and turning actions, meniscus tears—a critical type of cartilage in the knee joint—also happen often. The keys to avoiding these ailments and guaranteeing the longevity of an athlete are proper conditioning, warm-up activities, and rest.
How long does a tennis knee take to heal?
Depending on the extent of the injury and the patient’s capacity for recovery, tennis knee injuries can take several months to heal. For mild cases, adequate rest, ice, compression, and elevation can help them heal in a matter of weeks. Getting competent medical guidance and performing appropriate rehabilitation exercises is essential. Future injuries can be avoided by gradually restarting physical activity and rebuilding strength. Proactive measures can hasten the healing process.
What are the symptoms of tennis knees?
Tennis players frequently suffer from patellar tendonitis or jumper’s knee, which causes pain, soreness, and swelling near the patellar tendon. Exercises like sprinting, leaping, or stair climbing might make it worse. Early detection and treatment are essential to keep the illness from worsening.
How do you treat a tennis knee?
A complete strategy involving rest, ice treatment, compression bandages, physical therapy, cross-training exercises, and appropriate procedures is necessary for tennis knee injuries. Ice helps with stability and inflammation reduction while resting aids knee healing. Rehabilitation includes cross-training exercises, increased muscle strength, and increased flexibility. Wearing the right shoes and using the proper technique on the court helps to reduce knee stress and the chance of recurrent injuries.
Conclusion: Knee Injuries from Tennis
To avoid tennis-related knee problems, proper technique and strength training are essential. Targeted training improves the muscles surrounding the knee joint, resulting in stability. Purchasing superior tennis shoes lessens the impact on the knee. It’s critical to address discomfort swiftly. Tennis players can enjoy a healthy game and avoid knee injuries when conscious training is combined with prophylactics such as supporting equipment and self-care.




