Top 10 Tips: Managing Tibial Tubercle Pain in Adults

As we navigate the complex landscape of adult musculoskeletal health, one area that often goes overlooked is tibial tubercle pain in adults. While commonly associated with growing pains in adolescents, this elusive condition can also plague adults, causing discomfort and limitations in daily activities. From athletes to office workers, tibial tubercle pain can strike anyone at any time, making it a crucial topic for discussion in the realm of adult orthopedic health.
Contents
Understanding Tibial Tubercle Pain:
Definition:
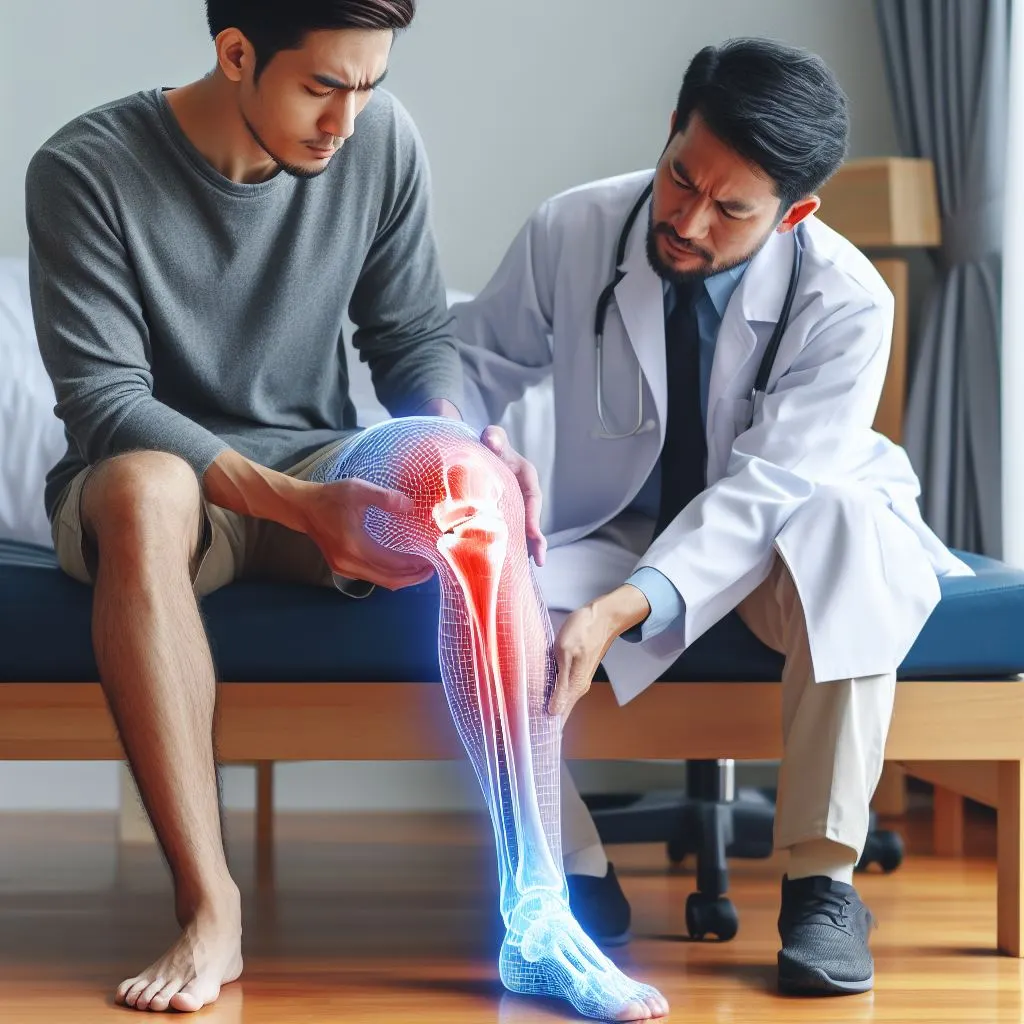
The bony projection situated beneath the knee joint on the anterior surface of the tibia is referred to as the tibial tubercle, or tibial tuberosity. It is essential for knee function and attaches the quadriceps muscles to the shinbone. It makes it possible for actions like walking, running, and jumping by transferring forces from the thigh muscles to the lower leg. To preserve patellar stability and avoid joint pain, the tibial tubercle must be positioned and aligned correctly.
Causes of pain:
Adults with jumper’s knee, or overuse or repetitive straining of the patellar tendon, frequently have tibial tubercle pain. Muscular imbalances and anatomical variances also cause discomfort. Inadequate rehabilitation and the creation of scar tissue can exacerbate pain from prior surgeries or traumas, causing persistent agony. Long-term comfort and optimal healing can result from identifying these issues and taking care of all the relevant aspects.
How to Heal a Torn Meniscus Naturally: A Comprehensive Guide
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Adults with jumper’s knee, or overuse or repetitive straining of the patellar tendon, frequently have tibial tubercle pain. Muscular imbalances and anatomical variances also cause discomfort. Inadequate rehabilitation and the creation of scar tissue can exacerbate pain from prior surgeries or traumas, causing persistent agony. Long-term comfort and optimal healing can result from identifying these issues and taking care of all the relevant aspects.
Identifying Symptoms:
It can be difficult to recognize and treat tibial tubercle discomfort, which is a severe pain in the knee that occurs during activities like running or climbing stairs. It can impair physical performance, causing annoyance and decreased mobility, particularly in athletes and energetic people. Self-diagnosis using online tools could miss underlying medical issues. Comprehending the subtleties of tibial tubercle pain is imperative for efficacious therapy and recuperation. Observing symptoms can assist people in seeking medical advice.
Diagnosis:
Osgood-Schlatter disease, also known as tibial tubercle pain, is diagnosed by physical examination and medical history. Modern imaging modalities, such as MRI and ultrasound, make it easier to spot structural abnormalities, which results in more precise diagnosis and individualized treatment regimens. Gait analysis employing motion capture technology can also help uncover movement anomalies and load distribution concerns, allowing for targeted interventions to improve functional movement patterns and minimize strain.
Top 10 Tips for Managing Tibial Tubercle Pain
- Stay Active: While it may be tempting to rest your leg completely, gentle physical activity can actually help manage pain and promote healing.
- Strengthen Your Muscles: Regular strength training, especially for the quadriceps, can help provide more support to the tibia and alleviate some of the stress on this bone.
- Apply Ice: Use an ice pack on the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time every few hours to reduce inflammation and ease pain.
- Use Pain Relievers: Non-prescription medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage acute pain episodes. Always take these as directed by a healthcare professional.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Shoes with good arch support and cushioning can help distribute weight evenly across your foot, reducing stress on the tibia.
- Try Physical Therapy: Working with a physical therapist can provide targeted exercises and stretches to relieve pain and improve function in the tibia.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintaining correct alignment while standing or walking can reduce strain on your bones and joints, including your tibial tubercle.
- Warm-Up Before Exercise: Always ensure you properly warm up before any strenuous physical activity to prevent injury and reduce strain on your tibia.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Carrying extra weight puts additional pressure on your lower legs which can exacerbate tibial tubercle pain.
- Consult a Specialist If Needed: If your pain is severe or continues despite self-care efforts, it may be time to consult an orthopedic specialist for further evaluation and treatment options.
Innovations in Treatment:

Latest Research:
Platelet-rich plasma injections, which lessen pain and enhance function, and strengthening activities aimed at the quadriceps and hamstrings are recent developments in the treatment of tibial tubercle pain. These non-invasive procedures support tissue restoration by utilizing the body’s inherent healing powers. In addition to treating the underlying causes of the symptoms, these treatments also improve the quality of life for those who are impacted in the long run.
Expert Opinions:
Knee pain has a substantial negative influence on quality of life and needs to be managed with professional guidance. When creating a treatment plan, it’s critical to take individual circumstances, underlying reasons, and medical history into account. Dr. David Patel, an expert in sports medicine, stresses early intervention with focused exercises, physical therapy, and assistive technology to avoid long-term harm and functional restrictions.
FAQ’s
Why does my tibial tubercle hurt?
Adults may experience acute knee discomfort from the tibial tubercle, a bony protrusion at the shinbone, as a result of repetitive strain injuries, Osgood-Schlatter disease, or patellar tendonitis. Biomechanical problems and other variables, such as muscular imbalances, might also be involved. This problem can be managed with imaging examinations, focused rehabilitation activities, and a comprehensive assessment by a medical practitioner.
Can I get Osgood-Schlatter as an adult?
Frequently linked to teenagers, Osgood-Schlatter disease can also strike adults, manifesting during a growth spurt and continuing until maturity. Changes in the anatomy of the knee or greater physical activity may cause the symptoms to return. Even adults who did not have Osgood-Schlatter during adolescence may still be at risk, particularly if they participate in activities that place an undue amount of strain on the tibial tubercle. Managing the illness may be made easier by being aware of its complexity.
What can cause a painful bony bump over the tibial tuberosity?
Why is there a bone sticking out below my knee?
One prevalent problem that causes discomfort and limits everyday activities is tibial tubercle pain. It may be brought on by overuse, recurrent strain, or a misaligned pelvis. Effective alleviation requires addressing the underlying reasons, which may include structural problems or muscle imbalances. Consulting with orthopedic doctors or physical therapists can help individuals receive individualized treatment regimens that improve their quality of life by restoring their mobility and comfort.
Soreness After Golf: 5 Tips to Prevent Soreness and Knee Pain
Conclusion: Tibial Tubercle Pain In Adults
In conclusion, tibial tubercle pain in adults can be a debilitating and challenging condition to manage. It often results from overuse or repetitive strain on the knee, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for addressing the underlying causes of the pain, which may include patellar tendonitis, Osgood-Schlatter disease, or other contributing factors. Patients should seek medical evaluation and customized treatment plans that may include physical therapy, activity modification, and in some cases, surgical intervention. By taking proactive steps to address tibial tubercle pain, individuals can improve their quality of life and regain functionality in their daily activities. Seeking professional guidance is crucial for managing this condition effectively.