Common Basketball Knee Injuries | Causes, Treatment and Prevention

I’m excited to share my expertise and provide you with valuable insights on this topic. Prepare to explore the specifics of these injuries, their causes, and the most effective ways to address them. We’ll also discuss practical steps you can take to minimize the risk of sustaining such injuries during your basketball knee injuries activities. Whether you’re a professional athlete, a recreational player, or simply someone passionate about the sport, this blog will provide you with the information required to keep your knees healthy and strong.
Contents
- 1 The Impact of Basketball on Knee Health
- 2 Common Basketball Knee Injuries
- 3 Prevention and Precaution
- 4 Treatment and Home Remedies
- 5 FAQ’s
- 5.1 What are the most common knee injuries in basketball?
- 5.2 How to treat knee injury from basketball?
- 5.3 What is a basketball knee?
- 5.4 Is a torn ACL common in basketball?
- 5.5 How common is an ACL tear in basketball?
- 5.6 What percent of NBA players tear their ACL?
- 5.7 Can a basketball player play with a torn ACL?
- 5.8 What sports are the highest in ACL tears?
- 5.9 What are the top 3 common injuries in basketball?
- 5.10 Why does my knee hurt after I play basketball?
- 5.11 How do you treat a basketball knee?
- 5.12 What is the most common knee injury in basketball?
- 5.13 What do NBA players put on their knees?
- 5.14 How do you heal your knees after basketball?
- 5.15 What is the fastest way to heal a knee injury?
- 5.16 How do NBA players deal with knee pain?
- 5.17 How long does it take for a knee injury to heal?
- 5.18 How do you prevent knee injuries in basketball?
- 5.19 Can basketball cause knee pain?
- 5.20 Does basketball cause knee pain?
- 5.21 What causes knee injuries in basketball?
- 5.22 Does brain functional connectivity contribute to musculoskeletal injury?
- 5.23 HOW ARE BASKETBALL INJURIES TREATED?
- 5.24 HOW CAN BASKETBALL INJURIES BE PREVENTED?
- 5.25 Preventing Basketball Knee Injuries
- 5.26 What Are Basketball Knee Injuries?
- 5.27 What are common basketball injuries?
- 6 Conclusion: Basketball Knee Injuries
The Impact of Basketball on Knee Health
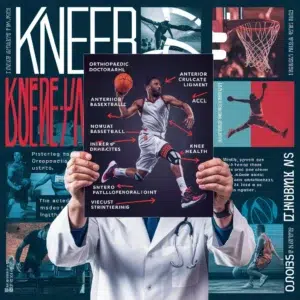
One of basketball’s most common knee injuries is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear. The ACL is a crucial ligament that stabilizes the knee joint, and it is often injured during sudden changes in direction or landing from a jump. ACL injuries can cause excruciating pain and may necessitate surgical intervention and extensive rehabilitation.
Secondly, basketball players are also susceptible to patellofemoral pain syndrome, commonly known as “runner’s knee.” This condition is characterized by pain around the kneecap (patella) due to repetitive stress and excessive strain on the patellofemoral joint during activities like jumping and running.
Thirdly, overuse injuries such as tendinitis and bursitis can also affect the knee joint in basketball players. Tendinitis refers to the inflammation of tendons around the knee, while bursitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion the knee joint.
Proper warm-up and stretching routines are essential to mitigate the impact of basketball on knee health. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles of the knee joint can aid in providing better support and stability. Proper footwear and the use of knee braces or sleeves can also help reduce the risk of knee injuries.
If a basketball player experiences persistent knee pain, seeking medical assistance from an orthopaedic specialist is crucial if there is discomfort or swelling. Appropriate treatment and early detection can stop more damage and aid in a successful recovery.
Steph Curry – Knee Injury case study
Common Basketball Knee Injuries
Here are some common knee injuries in basketball:
Jumper’s Knee (Patellar Tendinitis)
- Inflammation of the patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap to the shinbone.
- Caused by repetitive jumping and landing.
ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) Tears
- One of the most serious knee injuries in basketball.
- The ACL stabilizes the knee joint; tears often require surgery and lengthy rehabilitation.
Meniscus Tears
- Between the thigh and shin bones is a cartilaginous cushion called the meniscus.
- Tears can occur from sudden twisting or impact to the knee.
MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament) Sprains
- On the inside of the knee, the MCL joins the thigh bone to the shin bone.
- Sprains range from mild to severe, caused by impact to the outer knee.
Knee Bursitis
- Inflammation of the knee joint’s bursae are tiny sacs filled with fluid.
- Often caused by repetitive kneeling or direct impact to the knee.
Prevention involves proper warm-ups, strengthening exercises, and supportive knee braces or taping when necessary. Early treatment and rehabilitation are crucial for full recovery from these basketball-related knee injuries.
Prevention and Precaution
Precaution and prevention are essential for preserving optimal musculoskeletal health. Here are some important things to think about:
Prevention:
Regular exercise: To build muscle and increase joint flexibility, take up low-impact sports like cycling, swimming, or walking.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight increases joint stress and increases the risk of injuries and diseases like osteoarthritis.
Use proper technique: To prevent strains or overuse injuries, make sure to adopt proper form and technique when engaging in physical activity.
Warm-up and cool-down: Get your body ready for activity and give yourself time for a slow, steady cool-down to avoid strained or torn muscles.
Precaution:
Ergonomics: When lifting large objects or carrying out repetitive jobs, pay particular attention to your posture and body mechanics.
Protective gear: When playing sports or engaging in high-impact activities, wear the proper safety gear, such as braces, knee/elbow pads, or helmets.
Listen to your body: To avoid further harm or complications, get medical help as soon as possible if you are in constant pain or discomfort.
Rehabilitation: To speed up healing and avoid re-injury, adhere to the suggested rehabilitation regimen given by your healthcare professional if you suffer an injury.
Your overall joint and bone health can be preserved, and the risk of musculoskeletal injuries can be reduced by emphasizing prevention and following the appropriate safety measures.
Treatment and Home Remedies

FAQ’s
What are the most common knee injuries in basketball?
The most common knee injuries in basketball are ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tears, MCL (medial collateral ligament) tears, and patellar tendinitis.
How to treat knee injury from basketball?
Treatment for a knee injury from basketball depends on the specific injury but may include rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery.
What is a basketball knee?
“Basketball knee” is not a specific medical term. It may refer to a knee injury or condition related to playing basketball.
Is a torn ACL common in basketball?
Yes, a torn ACL is a common injury in basketball, particularly among athletes who engage in high-impact activities and sudden changes in direction.
How common is an ACL tear in basketball?
ACL tears are relatively common in basketball, particularly in competitive and high-impact play. They can occur due to sudden stops, pivots, or direct contact.
What percent of NBA players tear their ACL?
The percentage of NBA players who tear their ACL varies from season to season but is generally low compared to other sports. Exact statistics may vary.
Can a basketball player play with a torn ACL?
Playing with a torn ACL is possible but not recommended, as it can lead to further damage and instability in the knee. Surgery and rehabilitation are often necessary.
What sports are the highest in ACL tears?
Sports that involve pivoting, jumping, and sudden stops, such as basketball, soccer, and football, are among the highest in ACL tears.
What are the top 3 common injuries in basketball?
The top three common injuries in basketball are ankle sprains, knee injuries (including ACL tears), and finger injuries.
Why does my knee hurt after I play basketball?
Knee pain after playing basketball can be caused by overuse, improper technique, muscle imbalances, or an underlying injury. Rest, ice, and proper conditioning can help alleviate pain.
How do you treat a basketball knee?
Treatment for a basketball-related knee injury involves rest, ice, compression, elevation, and possibly physical therapy or surgery, depending on the severity of the injury.
What is the most common knee injury in basketball?
The most common knee injury in basketball is an ACL tear, followed by MCL and patellar injuries.
What do NBA players put on their knees?
NBA players may use various treatments on their knees, such as ice packs, compression sleeves, braces, and kinesiology tape, to manage pain and support the joint.
How do you heal your knees after basketball?
Rest, ice, compression, elevation, and physical therapy can be beneficial to heal knees after basketball. It’s essential to follow medical advice for the best recovery.
What is the fastest way to heal a knee injury?
The fastest way to heal a knee injury is to seek medical attention promptly, follow the prescribed treatment plan, and avoid activities that exacerbate the injury.
How do NBA players deal with knee pain?
NBA players deal with knee pain through various methods, including rest, physical therapy, strengthening exercises, and sometimes surgery for more severe cases.
How long does it take for a knee injury to heal?
The healing time for a knee injury varies depending on the severity and type of injury. Minor injuries may heal in a few weeks, while more severe injuries may take several months or longer.
How do you prevent knee injuries in basketball?
To prevent knee injuries in basketball, players should warm up properly, use proper technique, wear appropriate footwear, strengthen muscles around the knee, and maintain overall fitness.
Can basketball cause knee pain?
Yes, basketball can cause knee pain due to the high-impact nature of the sport, which can lead to overuse injuries, ligament strains, and other issues.
Does basketball cause knee pain?
Basketball can cause knee pain, particularly if players do not use proper technique, have muscle imbalances, or overuse their knees without proper rest and recovery.
What causes knee injuries in basketball?
Knee injuries in basketball can be caused by sudden stops, changes in direction, jumping, landing incorrectly, overuse, and direct impact on the knee.
Does brain functional connectivity contribute to musculoskeletal injury?
Brain functional connectivity may contribute to musculoskeletal injury by affecting movement patterns and coordination, leading to an increased risk of injury during physical activity.
HOW ARE BASKETBALL INJURIES TREATED?
Basketball injuries are treated based on their specific nature but often involve rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and sometimes surgery.
HOW CAN BASKETBALL INJURIES BE PREVENTED?
Basketball injuries can be prevented by warming up properly, using the correct technique, wearing appropriate footwear, strengthening muscles, and maintaining overall fitness.
Preventing Basketball Knee Injuries
Preventing basketball knee injuries involves strengthening the muscles around the knee, using proper jumping and landing techniques, wearing supportive footwear, and maintaining overall fitness.
What Are Basketball Knee Injuries?
Basketball knee injuries are injuries that occur in the knee while playing basketball, such as ACL tears, MCL tears, and patellar tendinitis.
What are common basketball injuries?
Common basketball injuries include ankle sprains, knee injuries (such as ACL tears), finger injuries, and muscle strains. Proper conditioning and technique can help prevent these injuries.
Conclusion: Basketball Knee Injuries
In Conclusion, we have discussed common basketball knee injuries, their causes, available treatments, and precautions to take. Basketball is a physically demanding activity that involves a lot of jumping, swerving, and abrupt direction changes, which makes knee injuries common in the sport. Players must comprehend the underlying causes of these ailments and adopt appropriate preventive measures to preserve their general well-being and longevity in the game. Basketball players can reduce their risk of knee injuries and guarantee a successful and injury-free career on the court by addressing risk factors, following recommended treatment procedures, and implementing efficient prevention strategies.




